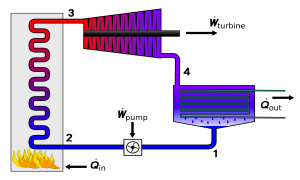
A thermal station could be a station within which heat is converted to power. In most, a steam-driven turbine converts heat to mechanical power as an intermediate to wattage. Water is heated, turns into steam and drives a turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine the steam is condensed during a condenser and recycled to where it had been heated. this is often called a Rankine cycle. The power plant on thermal energy plays a vital role in India to supply electricity.
The best variation within the design of thermal power stations is thanks to the various heat sources: fuel, energy, alternative energy, biofuels, and waste incineration are all used. Some thermal power plants also are designed to provide heat energy for industrial purposes, for district heating, or desalination of water, additionally to generating wattage.
Typical components of a coal-fired thermal power station
- Cooling tower
- Cooling water pump
- Transmission line (3-phase) heater
- Step-up transformer (3-phase)
- Electrical generator (3-phase)
- Low-pressure steam turbine
- Condensate pump (to deaerator)
- Surface condenser
- Intermediate pressure-pressure
- Steam control valve
- High-pressure steam turbine
- Deaerator
- Feedwater
- Coal conveyor
- Coal hopper
- The coal pulverizer
- Boiler steam drum
- Bottom ash hopper
- Superheater
- Forced draft fan
- High-pressure combustion air intake
- Economiser
- Air preheater
- Precipitators/dust collectors/scrubbers
- Induced draft fan
- Flue-gas stack
- Condensate pump (to the boiler)
Steps of Function
- First, into the furnace of the boiler, the burning of pulverized coal happens
- High-pressure steam is produced within the boiler.
- This steam is then gone through the superheater, where it further heated.
- This superheated steam is then entered into a turbine at high speed.
- In the turbine, this steam force rotates the turbine blades which means here within the turbine the stored mechanical energy of the high pressured steam is converted into energy.
- After rotating the turbine blades, the steam has lost its air mass, passes out of turbine blades and enters into a condenser.
- In the condenser, the cold water is circulated with the help of a pump which condenses the low wet steam.
- This condensed water is then further supplied to depression warmer where the air mass steam increases the temperature of this feed water, it's nevertheless heated during a high heater where the high of steam is employed for heating.
- The turbine in thermal power plant acts as a chief mover of the alternator.
Comment below if you have any questions
Recent post:
Post by Riju Sharma









1 Comments
😁😁😁
ReplyDeleteThank you for your feedback